Resource Pool Architecture
The Resource Manager handles resources as one or more resource pools, which are a pre-allocated subset of the system resources with an associated queue.
In Enterprise Mode, there is one global set of resource pools that apply to all subclusters in the entire database. In Eon Mode, you can allocate resources globally or per subcluster. Global-level resource pools apply to all subclusters. Subcluster-level resource pools allow you to fine-tune resources for the type of workloads that the subcluster does. If you have both global- and subcluster-level resource pool settings, you can override any memory-related global setting for that subcluster. Global settings are applied to subclusters that do not have subcluster-level resource pool settings. See Managing Workload Resources in an Eon Mode Database for more information about fine-tuning resource pools per subcluster.
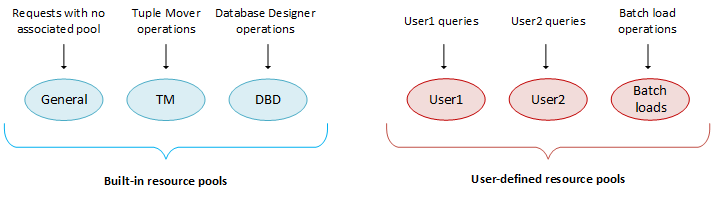
Vertica is preconfigured with a set of Built-In Pools that allocate resources to different request types, where the GENERAL pool allows for a certain concurrency level based on the RAM and cores in the machines.
Modifying and Creating Resource Pools
You can configure the built-in GENERAL pool based on actual concurrency and performance requirements, as described in Built-In Pools. You can also create custom pools to handle various classes of workloads and optionally restrict user requests to your custom pools.
You create and modify user-defined resource pools with CREATE RESOURCE POOL and ALTER RESOURCE POOL, respectively. You can configure these resource pools for memory usage, concurrency, and queue priority. You can also restrict a database user or user session to use a specific resource pool. Doing so allows you to control how memory, CPU, and other resources are allocated.
The following graphic illustrates what database operations are executed in which resource pool. Only three built-in pools are shown.